When building Java applications, localization is a valuable approach to making the app accessible to users across various regions.
What is localization
Localization is modifying how data is displayed depending on regions. It’s a very important factor when your app has international users. For developers, localizing the app achieves better user experience, which eventually leads to higher business potential. For example, the date format in US is mm/dd/yy (07/23/25), whereas in the UK it’s dd/mm/yy (23/07/25).
You may also need to consider translating your apps into different languages when necessary. In this blog, I’ll walk you through how to add a new language to a Java application that already supports localization, using our JPedal Java PDF Viewer as an example. JPedal Viewer is a fast and lightweight Java PDF and image viewer that allows you to embed PDF and image viewing capabilities into any Java client application.”
How to add language support in your Java app
[PREFIX]_[LANGUAGE ID].properties messages_en.properties // English
- Change the computer language setting directly
- Change the language programmatically with
Locale.setDefault(Locale.YourCountry) - Configure the application, for example, in IntelliJ, add this to your VM setting:
-Duser.language=[your language] -Duser.country=[your country]
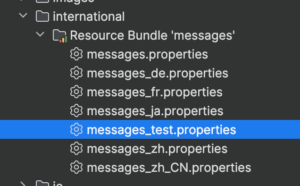
Our customers on JPedal OEM license have the access to the product source code. Therefore, they can simple copy the “org/jpedal/international/messages.properties” (this is a directory inside our jar structure and it is not on the file system), paste it into the same directory, rename it to their desired language, and change the values in the file.
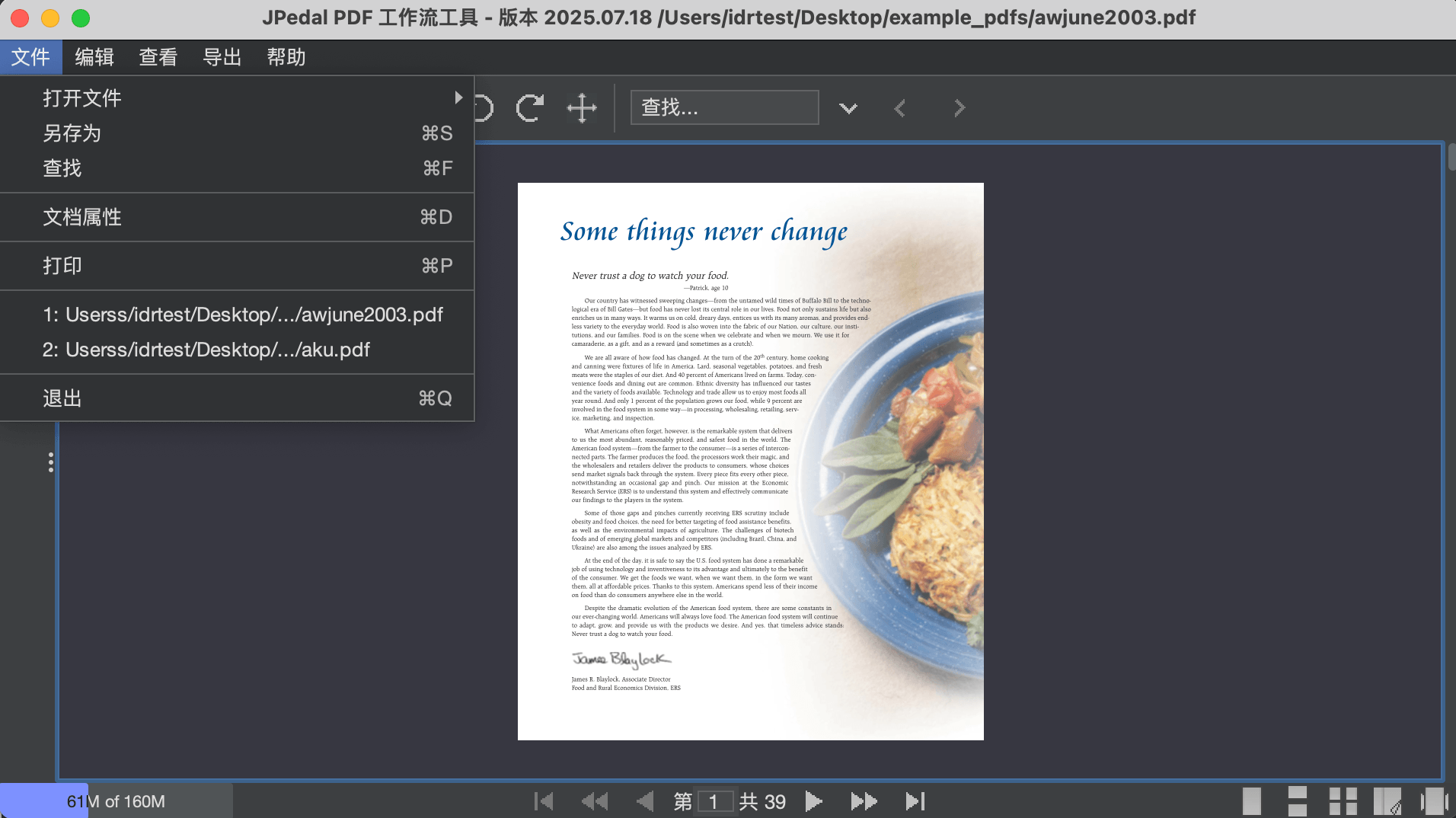
This is what the JPedal Viewer looks like in simplified Chinese:
How to add language support in a signed Java jar
We usually do not recommend modifying a signed jar, because doing so invalidates the digital signature, which defeats the entire purpose of signing the JAR in the first place.
However, if you absolutely have to do so, you should:
- Unjar the signed jar
jar xf xxx.jar - Follow the steps above
- Delete the .DSA file and sign it by yourself (if necessary)
- Rejar (if necessary)
jar cf xxx.jar
Conclusion
This tutorial walks you through how to localize a Java app with an example of adding your own language support in JPedal. Our JPedal Viewer is highly customizable: it uses international English as its default language but it makes full use of Java’s language l10n localization features. Currently, we provide out of the box support for English, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, French, German, and Japanese. Click here to try it out!